مواصفات الوصول لجافا
و يتم تنظيم إمكانية الوصول إلى الفئات "classes" ، و المشيدات "constructors" ، و المناهج "methods" و الحقول "fields" باستخدام محددات الوصول "Access Modifiers" بمعنى آخر الفئة يمكنها السيطرة على إمكانية الوصول إلى المعلومات أو البيانات الخاصة بها من قبل فئات أخرى. للاستفادة من عملية التغليف "encapsulation" ، فيجب الحد من إمكانية الوصول بأكبر قدر ممكن.
جافا يوفر عددا من محددات الوصول "Access Modifiers" لمساعدتك على ضبط مستوى الوصول الذي تريده للفئات "classes" فضلا عن الحقول "fields" و المناهج "methods" و المشيدات "constructors" في الفئات الخاصة بك. أي عضو "member" يصبح لديه حزمة "package" افتراضية أو وصول افتراضي عندما لا يتم تحديد محدد الوصول له.
محددات الوصول "Access Modifiers"
1. private
2. protected
3. default
4. public
محدد الوصول العام public
الحقول "fields" و المناهج "methods" و المشيدات "constructors" المعلن العامة "public" (الأقل تقييدا) ضمن فئة عامة "public" هي قابلة للوصول من طرف أي فئة في برنامج جافا ، سواء كانت هذه الفئات في نفس الحزمة "package" أو في حزمة أخرى.
محدد الوصول الخاص private
لا يمكن استخدام الحقول "fields" أو المناهج "methods" الخاصة "private" (الأكثر تقييدا) من قبل الفئات "classes" و الواجهات "Interfaces". فإنه أيضا لا يمكن للحقول "fields" أو المناهج "methods" داخل نفس الواجهة أن تستخدمهم. الحقول "fields" و المناهج "methods" و المشيدات "constructors" المعلن خاصة "private" تخضع لقيود الصارمة، مما يعني أنه لا يمكن الوصول إلىها من أي مكان خارج الطبقة. استراتيجية التصميم جعل جميع الحقول خاصة "private" و وفّرت لها مناهج عامة جالبة " getter methods".
محدد الوصول المحمي protected
لا يمكن استخدام الحقول "fields" أو المناهج "methods" المحمية "protected" من قبل الفئات "classes" و الواجهات "Interfaces". فإنه أيضا لا يمكن للحقول "fields" أو المناهج "methods" داخل نفس الواجهة أن تستخدمهم. الحقول "fields" و المناهج "methods" و المشيدات "constructors" المعلن محمية "protected" في الفئة الفائقة لا يمكن الوصول إليها إلا عن طريق الفئات الفرعية في حزم أخرى. يمكن للفئات الموجودة في نفس الحزمة أيضا الوصول إلى الحقول المحمية "protected fields" والمناهج المحمية و المشيدات المحمية كذلك ، حتى لو انهم ليسوا فئة فرعية لأعضاء الفئة المحميين.
محدد الوصول الافتراضي default
جافا توفر محدد افتراضي "default" الذي يستخدم عند عدم وجود أي محدد وصول "access modifier". أي فئة "class" ، أو مشيد "constructor" ، أو منهج "method" أو حقل "field" لا يوجد لديه محدد الوصول "access modifier" معلن فهو غير قابل للوصول إلا من خلال فئات موجودة في نفس الحزمة. لا يستخدم المحدد الافتراضي "default modifier" للحقول و المناهج الموجودة داخل الواجهة "interface".
أدناه هو برنامج لشرح استخدام محددات الوصول "access modifiers" العامة "public" والخاصة "private" و المحمية "protected" والافتراضية "default" أثناء عملية الوصول إلى الحقول "fields" و المناهج "methods". إخراج "output" كل واحد من هذه الملفات لجافا تصور لنا محددات الوصول لجافا.
الفئة الأولى هي SubclassInSamePackage.java التي هي موجودة في الحزمة pckage1 . ملف جافا يحتوي على الفئة الاساسية و الفئة الفرعية داخل محيط الفئة التي تنتمي إلى نفس الفئة كما هو مبين أدناه.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 | package pckage1;class BaseClass { public int x = 10; private int y = 10; protected int z = 10; int a = 10; //Implicit Default Access Modifier public int getX() { return x; } public void setX(int x) { this.x = x; } private int getY() { return y; } private void setY(int y) { this.y = y; } protected int getZ() { return z; } protected void setZ(int z) { this.z = z; } int getA() { return a; } void setA(int a) { this.a = a; }}public class SubclassInSamePackage extends BaseClass { public static void main(String args[]) { BaseClass rr = new BaseClass(); rr.z = 0; SubclassInSamePackage subClassObj = new SubclassInSamePackage(); //Access Modifiers - Public System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.x); subClassObj.setX(20); System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.x); //Access Modifiers - Public // If we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton // error as the fields and methods being accessed are private /* System.out.println("Value of y is : "+subClassObj.y); subClassObj.setY(20); System.out.println("Value of y is : "+subClassObj.y);*/ //Access Modifiers - Protected System.out.println("Value of z is : " + subClassObj.z); subClassObj.setZ(30); System.out.println("Value of z is : " + subClassObj.z); //Access Modifiers - Default System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.a); subClassObj.setA(20); System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.a); }} |
Output
Value of x is : 10
Value of x is : 20
Value of z is : 10
Value of z is : 30
Value of x is : 10
Value of x is : 20
الفئة الثانية هي SubClassInDifferentPackage.java التي هي موجودة في مجموعة مختلفة عن الفئة الأولى. تمتد هذه الفئة من الفئة لأولى (SubclassInSamePackage.java).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 | import pckage1.*;public class SubClassInDifferentPackage extends SubclassInSamePackage { public int getZZZ() { return z; } public static void main(String args[]) { SubClassInDifferentPackage subClassDiffObj = new SubClassInDifferentPackage(); SubclassInSamePackage subClassObj = new SubclassInSamePackage(); //Access specifiers - Public System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.x); subClassObj.setX(30); System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.x); //Access specifiers - Private // if we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton // error as the fields and methods being accessed are private /* System.out.println("Value of y is : "+subClassObj.y); subClassObj.setY(20); System.out.println("Value of y is : "+subClassObj.y);*/ //Access specifiers - Protected // If we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton // error as the fields and methods being accessed are protected. /* System.out.println("Value of z is : "+subClassObj.z); subClassObj.setZ(30); System.out.println("Value of z is : "+subClassObj.z);*/ System.out.println("Value of z is : " + subClassDiffObj.getZZZ()); //Access Modifiers - Default // If we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton // error as the fields and methods being accessed are default. /* System.out.println("Value of a is : "+subClassObj.a); subClassObj.setA(20); System.out.println("Value of a is : "+subClassObj.a);*/ }} |
Output
Value of x is : 10
Value of x is : 30
Value of z is : 10
الفئة الثانية هي ClassInDifferentPackage.java التي هي موجودة في مجموعة مختلفة عن الفئة الأولى. تمتد هذه الفئة من الفئة لأولى.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 | import pckage1.*;public class ClassInDifferentPackage { public static void main(String args[]) { SubclassInSamePackage subClassObj = new SubclassInSamePackage(); //Access Modifiers - Public System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.x); subClassObj.setX(30); System.out.println("Value of x is : " + subClassObj.x); //Access Modifiers - Private // If we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton // error as the fields and methods being accessed are private /* System.out.println("Value of y is : "+subClassObj.y); subClassObj.setY(20); System.out.println("Value of y is : "+subClassObj.y);*/ //Access Modifiers - Protected // If we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton // error as the fields and methods being accessed are protected. /* System.out.println("Value of z is : "+subClassObj.z); subClassObj.setZ(30); System.out.println("Value of z is : "+subClassObj.z);*/ //Access Modifiers - Default // If we remove the comments it would result in a compilaton // error as the fields and methods being accessed are default. /* System.out.println("Value of a is : "+subClassObj.a); subClassObj.setA(20); System.out.println("Value of a is : "+subClassObj.a);*/ }} |
Output
Value of x is : 10
Value of x is : 30
مستويات محددات الوصول
مستويات محددات الوصول تحدد ما إذا كان بإمكان الفئات الأخرى استخدام حقل "field" معين أو استدعاء منهج "method" معين. هناك مستويان من محددات الوصول:
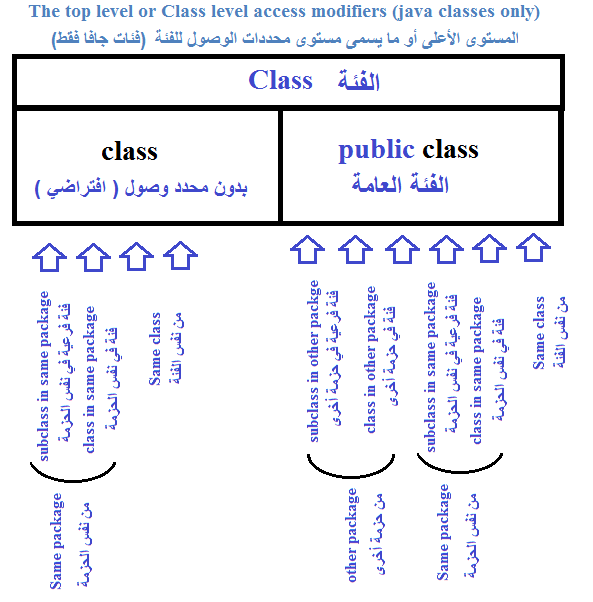
1- المستوى الأعلى أو ما يسمى مستوى محددات الوصول للفئة "Class level access modifiers" (فئات جافا فقط)
ولا يسمح سوى لإثنين من محددات الوصول هم العامة "public" و افتراضي (يعني عدم وجود أي محدد وصول)
- إذا كانت الفئة العامة "public" ، يمكن الوصول إليها من أي مكان.
- إذا كانت الفئة ليس لديها أي محدد وصول ، يمكن الوصول إليها إلا من نفس الحزمة فقط.
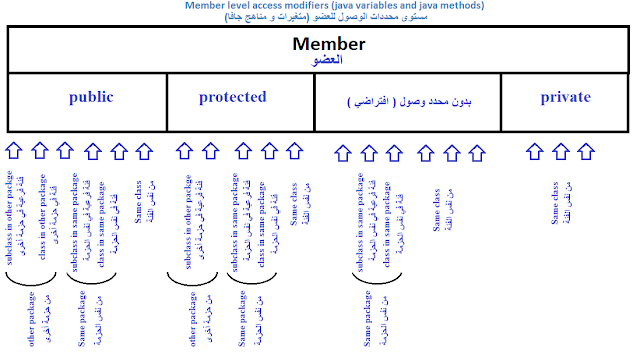
2- مستوى محددات الوصول للعضو (متغيرات و مناهج جافا)
يسمح لجميع محددات الوصول الأربعة وهم العامة "public"، الخاصة "private" ، محمية "protected" و الافتراضية (بدون محددات الوصول).
• إذا كان العضو عام "public" ، يمكن الوصول إليه من أي مكان.
• إذا كان العضو ليس لديه أي محدد وصول ، يمكن الوصول إليه إلا من نفس الحزمة فقط.
• إذا كان العضو خاص "private" -- يمكن للأعضاء فقط الوصول إليه.
• إذا كان العضو محمي "protected" -- يمكن الوصول إليه من "نفس الحزمة" و من أي فئة فرعية موجودة في أي حزم.
لفهم أفضل، هذه صياغة لمستوى محددات الوصول للعضو كجدول :
| Access Modifiers محددات الوصول |
Same Class نفس الفئة |
Same Package نفس الحزمة |
Subclass الفئة الفرعية |
Other packages الحزم الأخرى |
| public | Y نعم |
Y نعم |
Y نعم |
Y نعم |
| protected | Y نعم |
Y نعم |
Y نعم |
N لا |
| no access modifier | Y نعم |
Y نعم |
N لا |
N لا |
| private | Y نعم |
N لا |
N لا |
N لا |

ماذا عن محدد الوصول sync
ردحذف